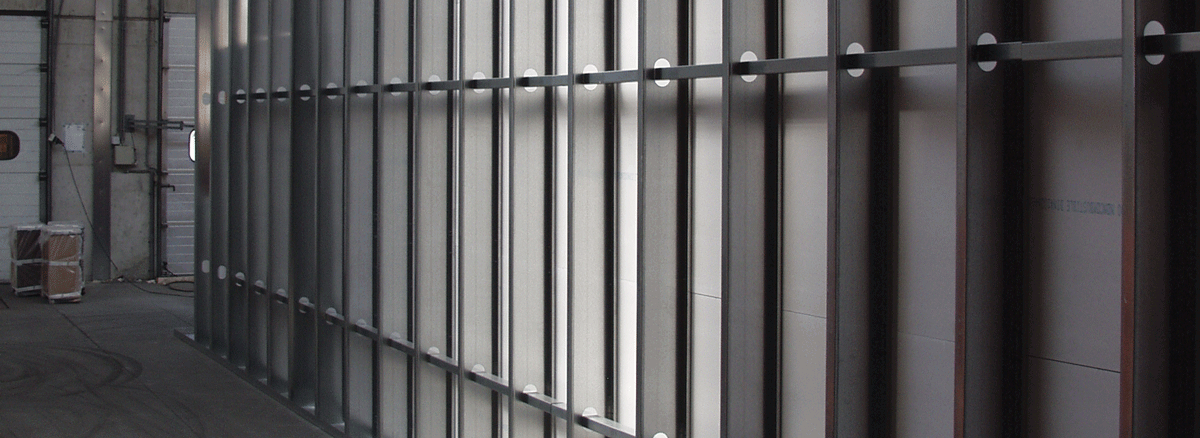

Fire partitions are all vertical and horizontal constructions in a building that form a boundary to stop fire propagation and therefore let the occupants escape safely and the fire brigade to start its intervention.
Keeping the fire under control by compartmentation
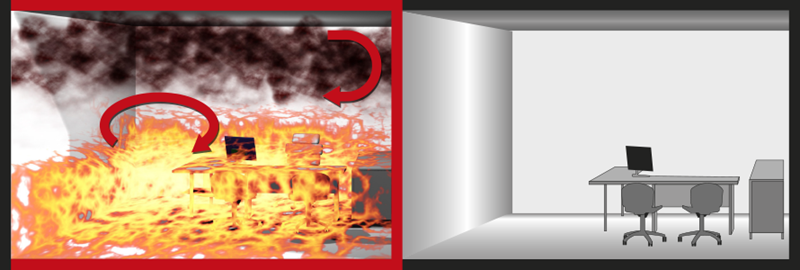
Any fire will start small and then grow. If sufficient combustible materials and oxygen are available, and no physical barriers limit the fire, it can quickly grow in size and temperature, and will eventually consume a part of the building, the complete building or even multiple buildings.
Fire safety measures aim to prevent such scenarios. It is difficult to control the quantity of combustible materials in a building, as the decoration and use of materials inside will often change throughout the life of the building, without thoroughly considering fire safety. Limiting the access of oxygen as a fire fighting strategy carries major risks, as toxic gases or combustible gas mixes may develop. For this reason, limiting the propagation of fire through a building is done by dividing the building into fire compartments. While the fire rages inside one compartment, in the remainder of the building the occupants have time to safely escape and the fire brigade has time to enter the building and intervene.
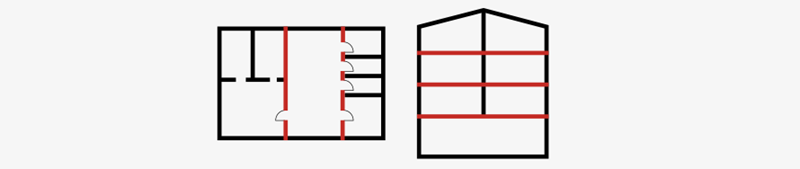
Each fire compartment is surrounded by boundaries that are fire resistant. This means that the boundaries have been designed and tested to avoid the spread of fire and hot gases to the adjacent compartment. These boundaries can be:
- vertical (walls, partitions, vertical membranes)
- horizontal (floors, ceilings, horizontal protective membranes).
The performance of the weakest boundary determines the time until the fire spreads to an adjacent compartment.
Integrity (E)
The vertical and horizontal constructions that form a boundary to stop the fire propagating are generally denoted as fire partitions. The location of partitions is determined by the building designer (or fire protection designer) in accordance with fire safety regulations, for example to limit each fire compartment to a certain maximum floor area or to protect an escape route.
Fire resistance criteria for partitions – how do partitions keep the fire locked up?
Partitions shall fulfill one or more of the following criteria to avoid fire propagation:
- E: Integrity – ability to stop flames and hot gases from penetrating.
- I: Insulation – ability to restrict the temperature rising on the cold side. In most cases, the temperature at the cold surface may not increase more than 140 degrees Celsius on average, or 180 degrees locally, compared to the initial temperature.
- R: Load-bearing function – ability of a structure to carry loads or actions without collapsing. Only applicable to partitions if the fire compartmentation boundary also has load-bearing functions.
The fire resistance is always expressed in minutes, usually in classes that are multiples of 30 minutes. For example, a load-bearing compartment floor that can withstand fire exposure of at least 90 minutes will be “REI 90”, and a sandwich (non-load-bearing) partition wall that keeps the flames out and temperatures low for at least 60 minutes will be “EI 60”.

Criteria E and I are intended to stop fire propagation. In case of only an “E” (integrity) requirement, the temperature of the unexposed surface can increase without restrictions. But if the unexposed surface reaches high temperatures, the combustible materials in the adjacent (non-fire) compartment may spontaneously ignite. This would cause the fire to spread to this compartment even before flames or hot gases penetrate the partition. To avoid this, the “I” (insulation) requirement is also required for fire compartments, escape routes, floors, etc.
In an element classified “EI” or, if load-bearing, “REI”, cold smoke may penetrate through the partition, as only hot gases are considered by the test standards. During a fire, the heat will activate, for example, intumescent materials in joints and penetration seals and create a tight boundary. But in the stage before the fire reaches the partition, the cold smoke may penetrate through it. This will normally not cause fire propagation, but smoke is often harmful to the occupants of a building. Avoiding smoke propagation is best done with products that tightly fit together without leaving gaps, preferably combined with a smoke extraction system to provide a way out for the smoke without building up overpressures.

Types of fire partitions
There are several test standards for horizontal and vertical partitions. Each test standard is related to a specific type of partition.
Vertical partitions
Non-load-bearing partition walls are often brick or concrete walls, sandwich partitions or shaft walls. In some cases, the existing walls need upgrading to become a fire partition or to meet the fire resistance rating asked for by the local regulations or the specifier. Even load-bearing walls, such as concrete walls, could need upgrading to increase the degree of fire resistance. Depending on the structural layout of a wall, its deformation during fire can be significant. Partition elements, and particularly fire protection materials, have to accommodate these deformations while continuing to perform.
For this reason, fire protection boards must always be tested in the relevant application. Joint finishings as tested shall be applied also in practice to make sure that integrity is maintained during fire.
The deflection is also strongly dependent on the height and width of the test specimen. Therefore, the scope of the test report or certificate must always clearly state the height and width limits allowable in practice. In the related European test standards, the maximum height in a fire test is usually 3 or 4 meters, given the size of most test furnaces. In some cases it is allowed to increase the height of the element by 1 meter above the tested height, if certain additional criteria are met during the fire test. To meet the market requests, high rise partition walls can either be tested at their actual height in some furnaces, or a calculation can be done, as based on specific codes for extrapolation to increased heights.
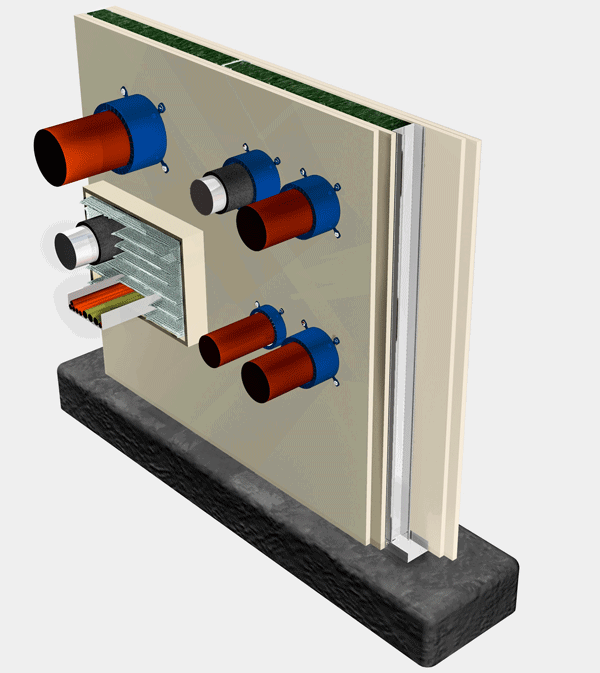
Most partition walls contain interruptions, such as pipe and cable penetrations that fully penetrate the wall, but also interruptions on one side of the wall, such as electricity sockets. Such interruptions are weak spots when it comes to fire resistance. Promat walls are tested along with solutions for sockets and other common interruptions, and we offer a wide range of penetration seals for cable and pipe penetrations.
All the partitions are tested in standard configurations, but there are always differences between the tested specimen and the application on site. Some of these differences are covered by direct field applications or by engineering judgments, but it is often necessary to do specific tests. For example, the corners of the walls, the connections between wall and slab, sprinkler supports or shelves hung on the walls must be fire tested.
All these "details" play a key role in fire safety, and must not be underestimated. For years we have been at the forefront in testing complex and real-world configurations, and can provide several solutions for each specific case.
In practice one critical element of a non-load-bearing partition wall is the connection of the partition wall to the ceiling or floor above. This connection needs to provide for some movement due to possible deformations of the partition wall as well as the floor above during a fire, but at the same time remain closed against fire. We thus developed specific wall header solutions to make sure that this movement is accommodated and that the fire does not propagate.

Horizontal partitions
Horizontal partitions can be tested in different ways, and this determines strongly how they will perform in practice. For this reason, it is necessary to select a fire protection system that is tested in a configuration that fits your specific needs.
In most national building code regulations there are requirements for “fire from below”: propagation from the compartment below to the compartment above. In some cases, there are also rules for “fire from above”: propagation from the compartment above to the compartment below. Both situations will affect the construction in very different ways, so they need to be tested separately.
The most often used horizontal compartmentations include:
- Independent ceilings (ceiling membranes)
- Incombustible or low combustible ceilings
- Suspended ceilings, which give a contribution to the fire resistance of load bearing elements (protective systems)
- Ceiling as component of a fire-rated roof constructions, with or without cavities.


